The SepView software also allows to compute the sedimentation velocities. These were used to investigate the concentration effect of the anionic dispersant (Fig. 4), the effect of blending the anionic dispersant with a nonionic surfactant (Fig. 5) and the effect of preparation conditions (Fig. 6).
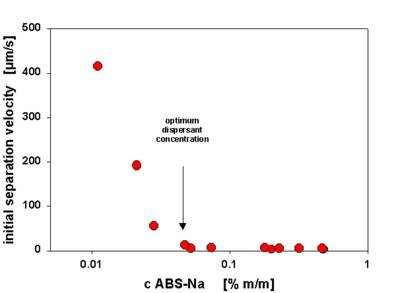
Fig. 4 Carbon black stabilization by an anionic dispersant - effect of dispersant concentration
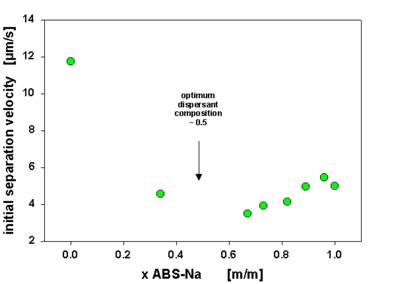
Fig. 5 Carbon black stabilization by an anionic-nonionic dispersant mixture - effect of anionic surfactant mass fraction (overall dispersant concentration 0.5 % m/m)
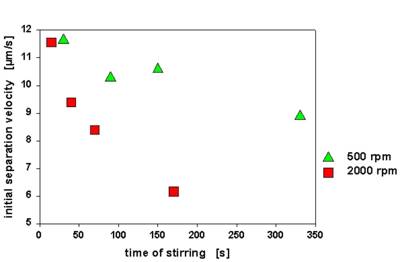
Fig. 6 Carbon black stabilization by an anionic dispersant (0.5 % m/m) - effect of stirring speed and time


No comments:
Post a Comment