Carbon blacks are widely applied as pigments and fillers in various products (inks, paints, rubber, plastics).
A multisample technique based on analytical centrifugation is described which allows for an accelerated study of dispersion stability without dilution, thus avoiding changes of dispersion properties.
The efficiency of this approach is demonstrated by selection of concentration and composition of stabilizing additives as well as of the preparation conditions for optimum stability.
Measurement principle
The LumiFuge measures the intensity of the transmitted light over the full sample length simultaneously as function of time. (Measurement scheme see Fig. 1)

Fig. 1 Lumifuge - Measurement scheme
The data are displayed as function of the radial position, as distance from the centre of the rotation (transmission profiles, see Fig. 2).
At the same time up to 8 different samples can be analysed simultaneously.
By means of the available analysis modes ‘Integral Transmission’ (Clarification) and ‘Front Tracking’ the separation behaviour of the individual samples can be compared and analysed in detail.
Experimental / Results
0.1 % m/m aqueous dispersions of carbon black were prepared with varying concentrations of sodium alkylbenzene sulfonate (ABS-Na) or with an anionic-nonionic surfactant mixture of varying composition. Further the influence of preparation conditions was evaluated.

Fig. 2 Evolution of transmission profiles with time - first recorded profile undermost, last profile uppermost, centrifugation of a carbon black suspension stabilized by a commercial anionic surfactant, 1500 rpm (285 x g).
The set of transmission profiles obtained for the dispersion stabilized by an alkylbenzene sulfonate is representative for the sedimentation of a polydisperse suspension. The sedimentation speed is inversely proportional to the stabilization achieved. Therefore, the stabilization effect can directly be visualized by comparing the kinetics of sedimentation (Fig.3).
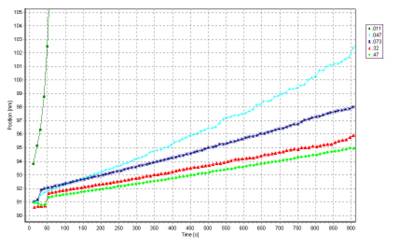
Fig. 3 Comparison of sedimentation kinetics (movement of boundary supernatant - suspension) obtained by the analysis mode ‘Front Tracking’, dependence on surfactant (ABS-Na) concentration (% m/m).
See the following Part II


No comments:
Post a Comment